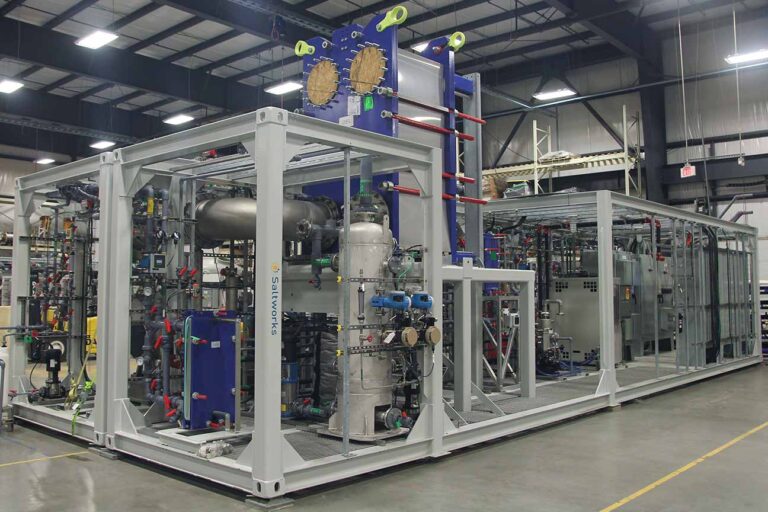

SaltMaker MVR & MSF Evaporative Crystallizers
Achieve true ZLD with two forced circulation evaporative crystallizer options: SaltMaker MVR and SaltMaker MSF.
Saltworks » Applications » Bio-Energy Wastewater Treatment
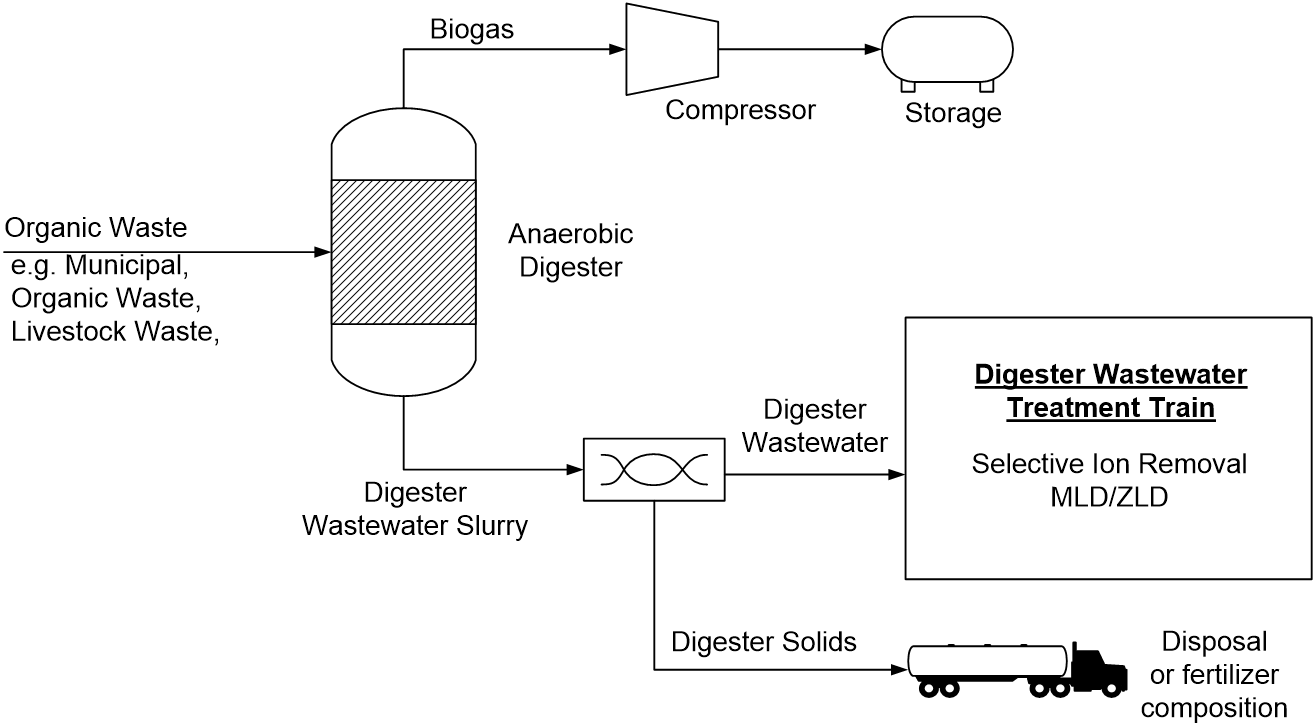
Biogas-producing anaerobic digesters produce methane gas from organic wastes. The methane can then be used in transportation, power generation, or heating. Digesters also produce wastewater, which cannot usually be re-used directly or discharged into a public sewer.
Depending on the digester feed and other factors, typical wastewater issues include total suspended solids (TSS), total dissolved solids (TDS), ammonia, biological oxygen demand (BOD), and chemical oxygen demand (COD). Depending on project needs, treatment involves the application of various technologies. Options range from reducing TSS and ammonia (nitrogen), to targeted selective contaminant removal of metals (e.g. zinc), up to a comprehensive ZLD process.
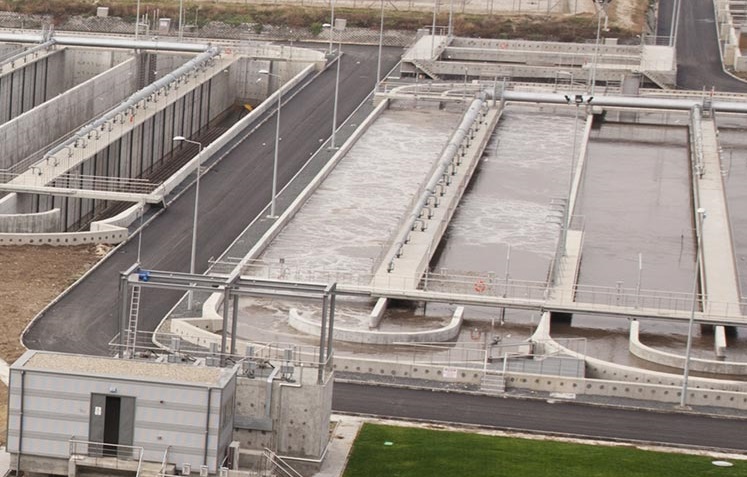


Achieve true ZLD with two forced circulation evaporative crystallizer options: SaltMaker MVR and SaltMaker MSF.
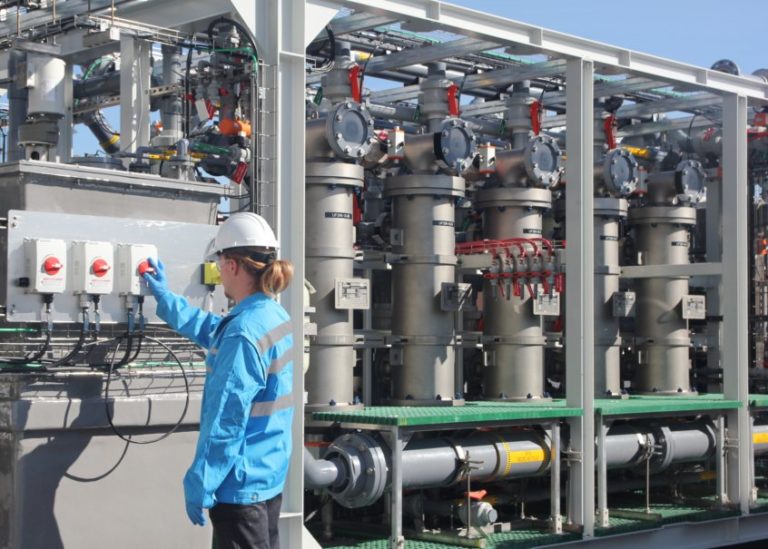

XtremeUF ceramic ultrafiltration removes oils, grease, precipitated by-products, particulate, microbes, and suspended solids.
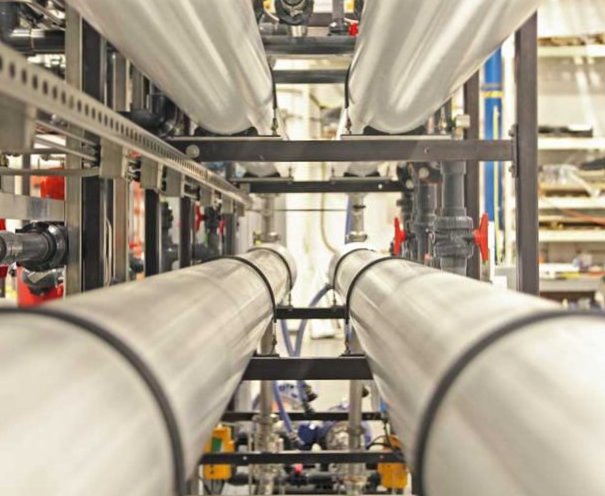

Our XtremeRO and OARO provide industry-leading recovery and reliablity. Concentrate brine, reduce discharge volumes, recover freshwater and more.

Water plays a critical role in ESG performance for many companies. With growing concerns around pollution ands consumption of water and energy, investing in responsible water management technology can improve your ESG profile and reduce operational risks.

There is no one-size-fits-all solution to removing ammonia from wastewater. Saltworks can help you understand your options, including hybridizing solutions with biological treatments to boost capacity and reliability, or provide entirely non-biological pathways.

Digester wastewaters are by-products of biogas production in anaerobic digesters. They require treatment prior to disposal. To meet regulation compliance, treatment options range from minor interventions such as selective contaminant removal, to major interventions such as minimum and zero liquid discharge (MLD/ZLD).
Excessive phenolic compounds are harmful to human health and the environment. Chlorophenols, by-products of chlorinating phenol-containing water, are carcinogens. A treatment system needs to be chosen and engineered carefully, with consideration of specific wastewater chemistry, operating conditions, and economics.